Table of contents
What is Docker?
Docker is a platform that enables software to run in its own isolated environment. SQL Server (from 2017) can be run on Docker in its own isolated container. Once Docker is installed, you simply download — or “pull” — the SQL Server on Linux Docker Image to your Mac, then run it as a Docker container. This container is an isolated environment that contains everything SQL Server needs to run.
Install Docker on macOS
Download Docker Desktop for Mac
This enables you to run SQL Server from within a Docker container.
Choose the right installation package
To download, visit the Docker CE for Mac download page and click Get Docker.
There are two types of installation packages provided. If you’re using Apple Silicon (M1/M2/M3), check your chip here and select the Apple Silicon build.
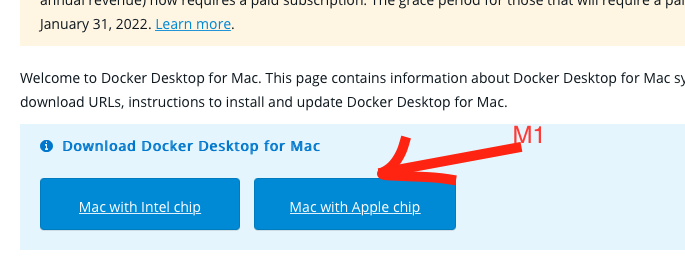
Install
Double-click the .dmg file and drag the Docker.app icon to your Applications folder.

Launch Docker
Launch Docker the same way you’d launch any other application (eg, via the Applications folder, the Launchpad, etc).
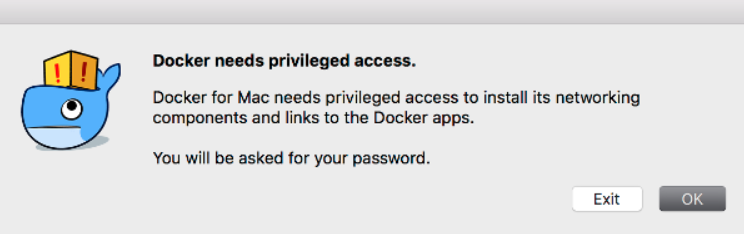
When you open Docker, you might be prompted for your password so that Docker can install its networking components and links to the Docker apps. Go ahead and provide your password, as Docker needs this to run.
Install Docker on Windows
Download Docker Desktop for Windows
Visit the Docker Desktop for Windows download page and click Get Docker.
Install
- Double-click
Docker Desktop Installer.exeto run the installer. - When prompted, choose your backend:
- Use WSL 2 (recommended) or Hyper-V, depending on system support.
- Follow the installation wizard to authorize and proceed.
- When the installation is successful, click Close.
- If your admin account is different from your user account, add the user to the
docker-usersgroup:- Open Computer Management (as administrator) → Local Users and Groups → Groups →
docker-users. - Right-click to add your user. Log out and log back in for changes to take effect.
- Open Computer Management (as administrator) → Local Users and Groups → Groups →